That is one other publish from an Financial Coverage Working Group assembly at Hoover, through which easy undergraduate provide and demand evaluation, creatively utilized, results in a stunning end result.
Casey Mulligan offered “Costs and Insurance policies in Opioid Markets.” Paper, slides and video of the presentation.
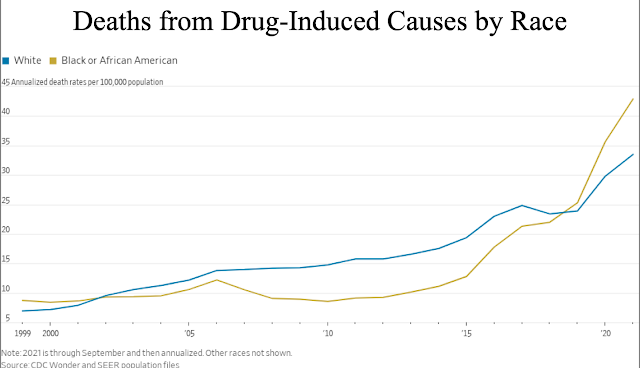
As soon as prescription opioids turned an evident disaster, the federal government took steps to limit the availability, elevating the worth. But opioid consumption and overdoses went up. Clarify that Mr. Chicago economist!
This is the intelligent reply:

There are two methods to purchase opioids, 1) legally or semi-legally; i.e. get opioids that come from pharmaceutical corporations and are prescribed to somebody by a health care provider or 2) illegally.
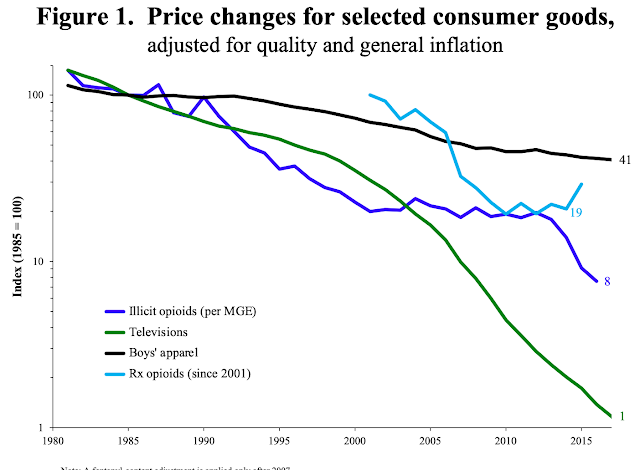
“Within the earlier years, opioid subsidies are created and expanded for sufferers and prescribers whereas rules are relaxed. In about 2010 insurance policies start to swing within the different course because the with reformulation (see under) and packages discouraging prescription provide to secondary markets. … enforcement of illicit-drug prohibitions was much less of a precedence between 2013 and 2016.
(i) heroin was considerably costlier per MGE than Rx opioids within the 1990s, (ii) illicit opioids turned cheaper over time, particularly since 2013, and in the end cheaper than Rx opioids, and (iii) starting in about 2011, Rx opioids turned costlier or troublesome to entry for nonmedical use as a result of regulatory and monetary modifications.